Wild lions currently exist in sub-Saharan Africa and in Asia (Gir Forest Sanctuary of India). The lion is a vulnerable species with sadly numbers dwindling year on year due to habitat loss and poaching.
Best Lion Conservation Programs
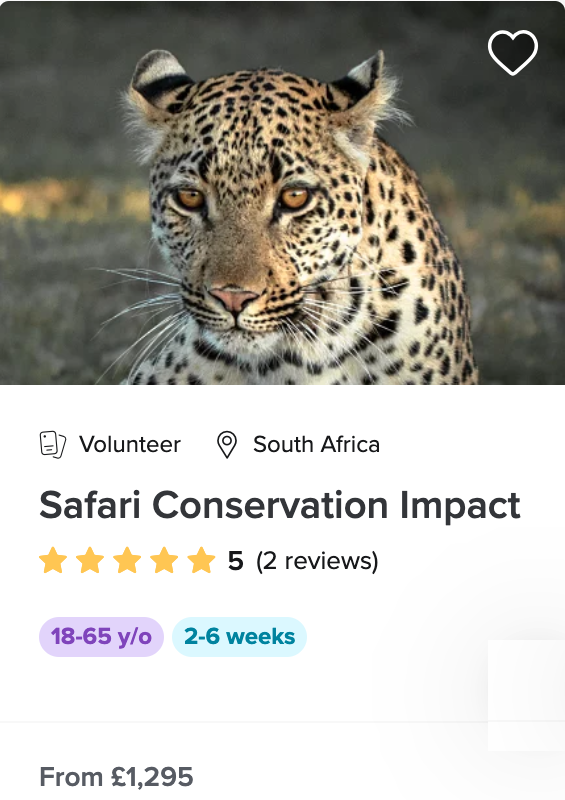
About Lions
The lion (Panthera leo) is a member of the cat family and is also called “the king of the animals”. The Swahili word for lion, “simba” means “king,” “strong,” and “aggressive.” Lions have muscular body covered with beautiful fur, strong legs with sharp claws and long tail. The lion is the second-largest living cat after the tiger.
Interesting Facts about Lions
- Their primary habitat of the African Lion is grassy plains, savanna and open woodlands.
- A lion’s roar can be heard up to 5 miles away.
- A lioness usually gives birth to 1-6 cubs in a litter.
- Lions are mostly nocturnal.
- Males lions stay with a pride only as long as they are strong enough to defend their group from other males.
Behaviour
Lions are found in savannas, grasslands and woodlands. Lions spend 16 to 20 hours a day sleeping and resting; they are more active at night, when they go hunting.
Females do most of the hunting, often hunting in groups to stalk and ambush prey. Lions hunt antelopes, zebras, giraffes and other herding animals. They will also feed on smaller animals such as hares, birds and reptiles.
The lion is the only social member of the cat (Felidae) family. Lions live in small groups called “prides” made of 20 to 30 members. The home territory of a pride can cover 100 square miles. All females in a pride are related to one another. Lions have very good sight, a sharp sense of hearing and good sense of smell.
Reproduction
Lions become sexually mature around the age of 2 to 3 years. They can copulate up to 40 times in a 24 hours period. Lions give birth to 1-6 cubs after a gestation period of about 15 weeks. Cubs are born blind. They begin hunting at 11 months but will remain with their mother for at least 2 years.